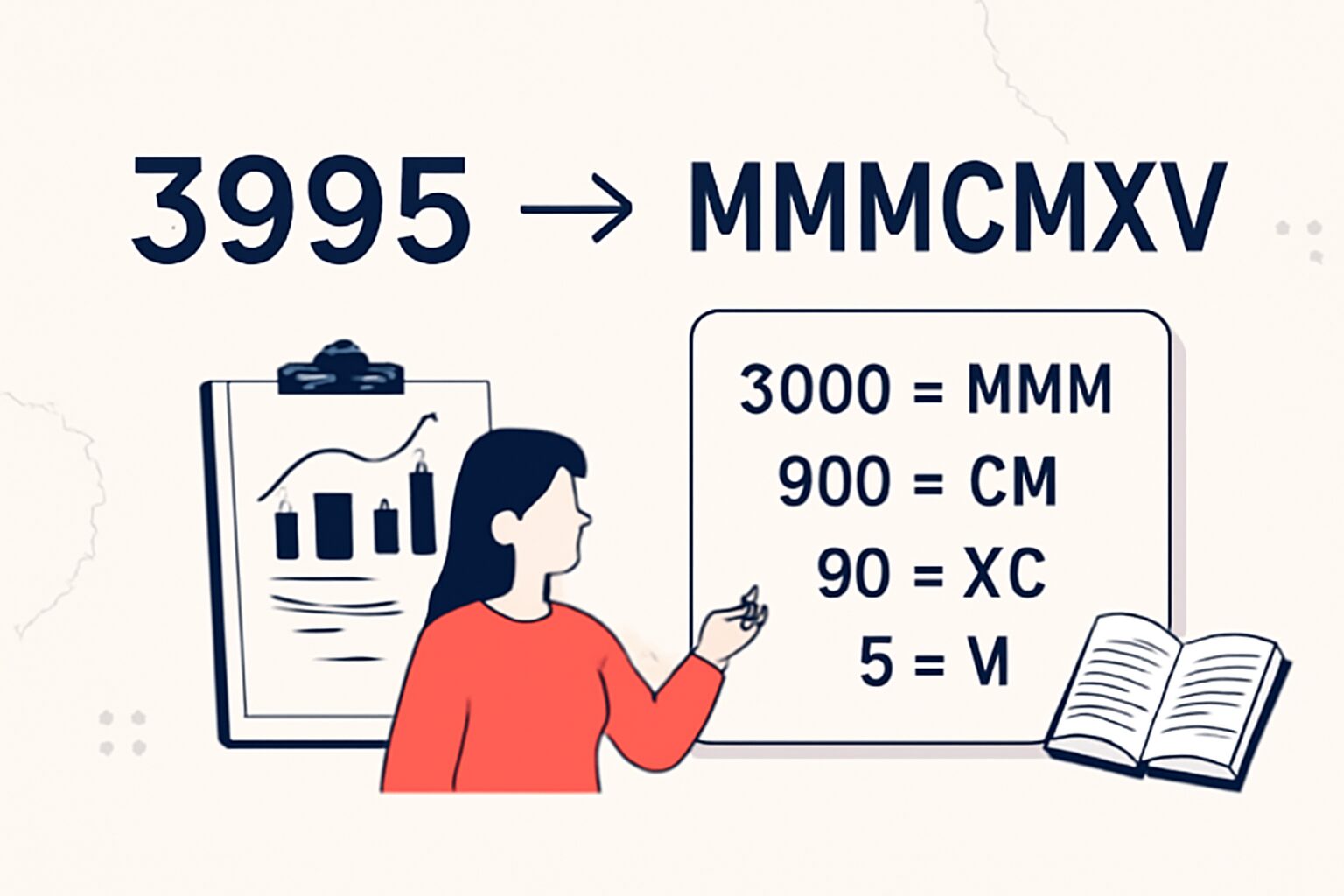
How to Convert 150 into Roman Numerals
Roman numerals are made up of seven letters: I (1), V (5), X (10), L (50), C (100), D (500), and M (1000). To write a number like 150, we combine these letters starting from the largest value and working down to the smallest.
Let's break 150 into parts and build the Roman numeral step by step:
100 fits into what's left of the number one time.
That means we add C to our Roman numeral because one × one hundred equals 100.
50 fits into what's left of the number one time.
That means we add L to our Roman numeral because one × fifty equals 50.
Final Answer
After combining all the parts, the Roman numeral for 150 is:
CL
Tip: If a smaller numeral appears before a larger one (like IV), it means you subtract. If a smaller one comes after a larger one (like VI), it means you add. You'll see both styles when needed.
How to Convert the Roman Numeral CL into a Normal Number
To convert a Roman numeral to a normal number, we read it from left to right and add up the values of each symbol. However, if a smaller symbol appears before a larger one, we subtract the smaller value instead of adding it.
Let's break down CL step by step:
Step 1: We see C, which means we add one hundred (add 100).
Step 2: We see L, which means we add fifty (add 50).
Total calculation: C (100) + L (50) = 150
Final Answer
The normal number for the Roman numeral CL is:
150
Tip: Remember the key rule - if a smaller numeral appears before a larger one (like IV), subtract the smaller value. If a smaller one comes after a larger one (like VI), add the values together.
What happened in the year 150?
In the year 150, Antoninus Pius was Roman Emperor, presiding over a relatively peaceful and prosperous period known as the Pax Romana.
In the year 150, Ptolemy completed his influential work, the Almagest, which became the cornerstone of astronomy for over a millennium.
In the year 150, the city of Teotihuacán in Mesoamerica reached its peak, with the Pyramid of the Sun standing as one of the largest structures in the pre-Columbian Americas.
In the year 150, the Satavahana dynasty in India continued to flourish, promoting trade and cultural exchanges along the Deccan region.
In the year 150, the Han Dynasty in China saw advancements in papermaking, contributing to the spread of literacy and bureaucratic efficiency.